中国组织工程研究 ›› 2015, Vol. 19 ›› Issue (35): 5697-5704.doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.2015.35.023
• 骨与关节图像与影像 bone and joint imaging • 上一篇 下一篇
基于3D打印齿状突空心钉置入的数字化导航
陈宣煌1,张国栋1,吴长福1,林海滨1,陈 旭1,余正希1,孙宇庆2
- 1福建医科大学教学医院,南方医科大学附属莆田医院,莆田学院附属医院骨科,福建省莆田市 351100;2北京大学第四临床医学院,北京积水潭医院脊柱外科,北京市 100035
-
收稿日期:2015-06-18出版日期:2015-08-27发布日期:2015-08-27 -
通讯作者:孙宇庆,博士,北京大学第四临床医学院,北京积水潭医院脊柱外科,北京市 100035 -
作者简介:陈宣煌,男,1975年生,汉族,福建省人,2007年福建医科大学毕业,硕士,副主任医师,主要从事数字化骨科学研究。
Odontoid cannulated screw fixation using digital navigation based on three-dimensional printing technique
Chen Xuan-huang1, Zhang Guo-dong1, Wu Chang-fu1, Lin Hai-bin1, Chen Xu1, Yu Zheng-xi1, Sun Yu-qing2
- 1 Department of Orthopedics, Teaching Hospital of Fujian Medical University; Affiliated Putian Hospital of Southern Medical University; Affiliated Hospital of Putian University, Putian 351100, Fujian Province, China
2 Department of Spine Surgery, the Fourth Clinical Medical College of Peking University, Beijing Jishuitan Hospital, Beijing 100035, China
-
Received:2015-06-18Online:2015-08-27Published:2015-08-27 -
Contact:Sun Yu-qing, M.D., Department of Spine Surgery, the Fourth Clinical Medical College of Peking University, Beijing Jishuitan Hospital, Beijing 100035, China -
About author:Chen Xuan-huang, Master, Associate chief physician, Department of Orthopedics, Teaching Hospital of Fujian Medical University; Affiliated Putian Hospital of Southern Medical University; Affiliated Hospital of Putian University, Putian 351100, Fujian Province, China
摘要:
背景:齿状突骨折因部位特殊,毗邻重要解剖结构,置钉难度大,稍有偏移亦可能导致内固定强度下降甚至失效。提高置钉的安全性和准确性,确定方便推广实施的个体化手术显得尤为重要。 目的:探讨Mimics软件数字化设计结合3D打印模块进行齿状突空心钉置入导航的方法,探讨其可行性及准确性。 方法:将16具人尸体颈椎标本进行连续薄层CT扫描,采集Dicom格式图像。Mimics软件予以三维重建,设计C2椎体齿状突空心钉置钉钉道及支撑柱、分割可剥离骨面,设计带钉道的导航模块并3D打印。导航模块在尸体标本上进行置钉导航,观察卡位、置钉情况,以X射线、CT扫描评价置钉效果。 结果与结论:共制作16个导航模块,植入22枚螺钉,观察钉道及置钉后椎体周围骨质,未见爆裂。术后行X射线、CT扫描重建,发现所有螺钉的进钉点,进钉方向、长度均与Mimics软件中模拟的预定理想进钉点、方向和长度一致,导航模块和相对应的椎体前方骨性结构贴合紧密,嵌合度良好,在应用时卡位及稳定性良好。结果证实,在导航模块的辅助下,前路齿状突空心钉置钉精准。基于3D打印的数字化技术有望良好实现骨科内固定物置入导航并普及应用。
中国组织工程研究杂志出版内容重点:人工关节;骨植入物;脊柱;骨折;内固定;数字化骨科;组织工程
中图分类号:
引用本文
陈宣煌,张国栋,吴长福,林海滨,陈 旭,余正希,孙宇庆. 基于3D打印齿状突空心钉置入的数字化导航[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2015, 19(35): 5697-5704.
Chen Xuan-huang, Zhang Guo-dong, Wu Chang-fu, Lin Hai-bin, Chen Xu, Yu Zheng-xi, Sun Yu-qing. Odontoid cannulated screw fixation using digital navigation based on three-dimensional printing technique[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research, 2015, 19(35): 5697-5704.
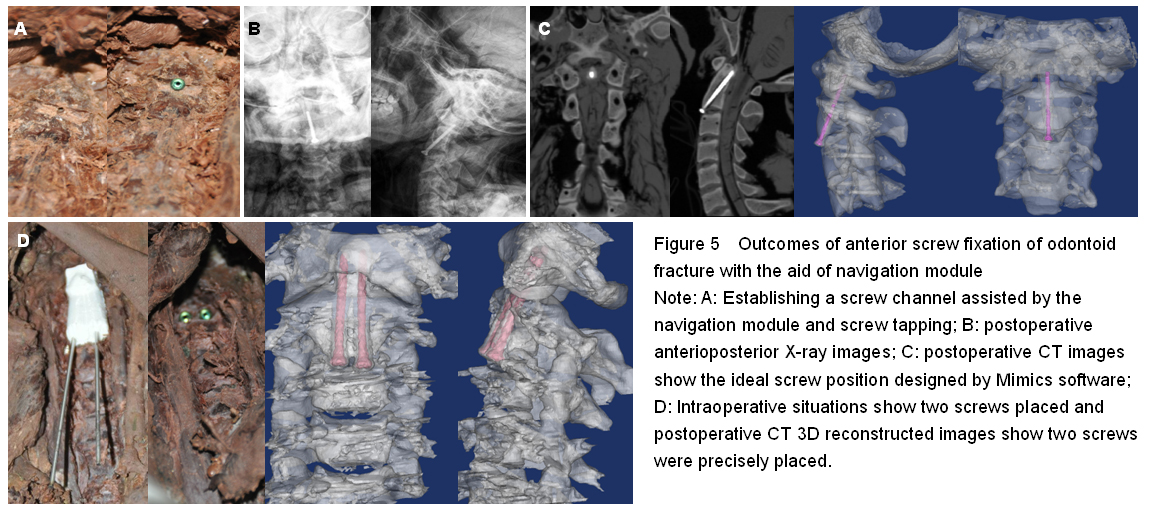
A total of 16 specimens were included in the final analysis, no drop out.
Totally 16 navigation modules were built and 22 screws were implanted. After screw placement, the cortical bone along screw channel and surrounding the C2 vertebral body was not cracked. Postoperative X-ray and CT scans showed that the factors regarding screw placement such as entry point, orientation and depth of placement were consistent with those ideal parameters simulated by Mimics software.
| [1] Rajasekaran S, Kamath V, Avadhani A. Odontoid anterior screw fixation. Eur Spine J. 2010;19(2):339-340. [2] Fountas KN, Kapsalaki EZ, Karampelas I, et al. Results of long-term follow-up in patients undergoing anterior screw fixation for type II and rostral type III odontoid fractures. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2005;30(6):661-669. [3] Pryputniewicz DM, Hadley MN. Axis fractures. Neurosurgery. 2010;66(3 Suppl):68-82. [4] Böhler J. Screw-osteosynthesis of fractures of the dens axis (author's transl). Unfallheilkunde. 1981;84(6):221-223. [5] Koller H, Acosta F, Forstner R, et al. C2-fractures: part II. A morphometrical analysis of computerized atlantoaxial motion, anatomical alignment and related clinical outcomes. Eur Spine J. 2009;18(8):1135-1153. [6] Osti M, Philipp H, Meusburger B, et al. Analysis of failure following anterior screw fixation of Type II odontoid fractures in geriatric patients. Eur Spine J. 2011;20(11):1915-1920. [7] Brown GA, Firoozbakhsh K, DeCoster TA, et al. Rapid prototyping: the future of trauma surgery? J Bone Joint Surg Am. 2003;85-A Suppl 4:49-55. [8] Paiva WS, Amorim R, Bezerra DA, et al. Aplication of the stereolithography technique in complex spine surgery. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2007;65(2B):443-445. [9] Xie A, Fang C, Huang Y, et al. Application of three-dimensional reconstruction and visible simulation technique in reoperation of hepatolithiasis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2013;28(2):248-254. [10] White AP, Hashimoto R, Norvell DC, et al. M orbidity and mortality related to odontoid fracture surgery in the elderly population. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2010;35(9 Suppl): S146-S157. [11] Dantas FL, Prandini MN, Caires AC, et al. Management of odontoid fractures using anterior screw fixation: analysis of 15 cases. Arq Neuropsiquiatr. 2002;60(3B):823-829. [12] Ochoa G. Surgical management of odontoid fractures. Injury. 2005;36 Suppl 2:B54-864. [13] Song KJ, Lee KB, Kim KN. Treatment of odontoid fractures with single anterior screw fixation. J Clin Neurosci. 2007; 14(9):824-830. [14] Agrillo A, Russo N, Marotta N, et al. Treatment of remote type ii axis fractures in the elderly: feasibility of anterior odontoid screw fixation. Neurosurgery. 2008;63(6):1145-1150. [15] Omeis I, Duggal N, Rubano J, et al. Surgical treatment of C2 fractures in the elderly: a multicenter retrospective analysis. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2009;22(2):91-95. [16] Chiba K, Fujimura Y, Toyama Y, et al. Treatment protocol for fractures of the odontoid process. J Spinal Disord. 1996;9(4): 267-276. [17] Wang MY. Cervical crossing laminar screws: early clinical results and complications. Neurosurgery. 2007;61(5 Suppl 2):311-325. [18] Lantada AD, Morgado PL. Rapid prototyping for biomedical engineering: current capabilities and challenges. Annu Rev Biomed Eng. 2012;14:73-96. [19] Magarelli N, Milano G, Baudi P, et al. Comparison between 2D and 3D computed tomography evaluation of glenoid bone defect in unilateral anterior gleno-humeral instability. Radiol Med. 2012;117(1):102-111. [20] Wu ZX, Huang LY, Sang HX, et al. Accuracy and safety assessment of pedicle screw placement using the rapid prototyping technique in severe congenital scoliosis. J Spinal Disord Tech. 2011;24(7):444-450. [21] Uehara M, Takahashi J, Hirabayashi H, et al. Computer-assisted C1-C2 Transarticular Screw Fixation "Magerl Technique" for Atlantoaxial Instability. Asian Spine J. 2012;6(3):168-177. [22] Hu Y, Yuan ZS, Spiker WR, et al. Deviation analysis of C2 translaminar screw placement assisted by a novel rapid prototyping drill template: a cadaveric study. Eur Spine J. 2013;22(12):2770-2776. |
| [1] | 鲁德志, 梅 钊, 李向磊, 王彩萍, 孙 鑫, 王孝文, 王金武. 3D打印脊柱侧凸矫形器的数字化设计及效果评估[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1329-1334. |
| [2] | 张同同, 王中华, 文 杰, 宋玉鑫, 刘 林. 3D打印模型在颈椎肿瘤手术切除与重建中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1335-1339. |
| [3] | 王德斌, 毕郑刚. 尺骨鹰嘴骨折-脱位解剖力学、损伤特点、固定修复及3D技术应用的相关问题[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(9): 1446-1451. |
| [4] | 吴 刚, 陈建文, 王世隆, 段笑然, 刘海军, 董建峰. 单纯HyProCure跗骨螺钉治疗青少年柔韧性平足合并痛性副舟骨[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(6): 901-905. |
| [5] | 孔令宝, 吕 欣. 胫骨后外侧平台骨折手术治疗中植入物选择与入路对支撑作用的影响[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(6): 942-947. |
| [6] | 刘正蓬, 王雅辉, 张义龙, 明 颖, 孙志杰, 孙 贺. 3D打印椎间融合器置入治疗脊髓型颈椎病:颈椎曲度及椎间高度恢复的半年随访[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(6): 849-853. |
| [7] | 徐俊马, 喻岳超, 刘 智, 刘 雨, 王飞通. 3D打印共面模板结合固定针技术在肺小结节经皮精准活检中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(5): 761-764. |
| [8] | 李兴平, 肖东琴, 赵 桥, 陈 硕, 白亦光, 刘 康, 冯 刚, 段 可. 钛表面载铜抗菌功能膜的制备及性能[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(4): 553-557. |
| [9] | 吴子健, 胡昭端, 谢有琼, 王 峰, 李 佳, 李柏村, 蔡国伟, 彭 锐. 3D打印技术与骨组织工程研究文献计量及研究热点可视化分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(4): 564-569. |
| [10] | 吕家兴, 白磊鹏, 杨朝昕, 苗岳松, 金 宇, 李哲宏, 孙广普, 徐 莹, 张擎柱. 膝关节骨性关节炎老年股骨转子间骨折行股骨近端防旋髓内钉内固定评价[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(3): 391-396. |
| [11] | 黄幼怡, 袁 伟. 3D打印技术在足踝外科骨折及畸形类疾病中的应用[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(3): 438-442. |
| [12] | 刘 畅, 韩树峰. 股骨近端联合拉力交锁髓内钉与股骨近端防旋髓内钉、亚洲型股骨近端防旋髓内钉内固定治疗老年转子间骨折的Meta分析[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(3): 477-485. |
| [13] | 吕泽祥, 吴居泰, 蒋 健, 冯 骁, 李腾飞, 王业华. 氨甲环酸联合卡络磺钠干预全膝关节置换的失血及安全性[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(3): 386-390. |
| [14] | 孟令杰, 钱 辉, 盛晓磊, 陆剑锋, 黄建平, 祁连港, 刘宗宝. 3D打印建模联合骨水泥成形微创治疗塌陷Sanders Ⅲ型跟骨骨折[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(24): 3784-3789. |
| [15] | 胡 靖, 向 阳, 叶 川, 韩子冀. 3D打印辅助与徒手置钉经皮椎弓根钉内固定治疗胸腰椎骨折的1年随访[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2021, 25(24): 3804-3809. |
biomechanics, high bone fusion rate, little influences on postoperative activities of the neck, and low costs, which better solves the contradiction between stable reduction of fractures and range of motion[5].
This was a method validation study.
Time and setting
The study was performed in the Department of Orthopedics, Affiliated Putian Hospital of Southern Medical University from January to June 2014.
Sixteen formalin-soaked adult cadaveric cervical spines without odontoid vertebra fracture, bony structure defects or space-occupying lesions were included in this study. These specimens (10 males and 6 females, with mean age at death 48.6 years, range, 36-71 years) were provided by Center for Clinical Anatomical Research of PLA Nanjing Military Region, China. Single screw implantation was performed in 10 human cadaveric cervical spines and double screw implantation in 6 human cadaveric cervical spines.
Specimen management
CT scanning: Human cadaveric cervical spines were scanned by 128-slice CT scanner using the scan parameters including tube voltage 130 kV, tube current 37.8 mAs, and slice thickness 0.75 mm. DICOM images (512 pxl × 512 pxl) were saved.
DICOM images of CT scans of the cervical spine were directly read, imported and organized by Mimics 14.0 software. Thresholding can be used to create selection masks. That is to say, without compromising the appearance of three-dimensional modules, thresholds can be decreased, extremely low threshold value possibly leads to an increase in mask pixel, and extremely high threshold value may result in a decrease in mask pixel. In this study, the threshold values were designated according to the Bone (CT) Scale in Mimics, i.e., 226-1 448 Hu. Segmentation of adjacent vertebrae was performed. The redundant data of each fault image were discarded by selective processing and noise reduction. Three-dimensional models of the cervical vertebrae were primarily acquired. Three-dimensional reconstruction of Mask was performed for better understanding surgical process and surgical location. Specific regions of interest can be edited with 3D tools using Mimics medical image processing software to separate individually and specify any color. The masks and 3D models created during all processes should be named in time to avoid errors. The temporally generated masks and 3D models can be deleted.
Using the “MedCAD module” of Mimics software, a “Cylinder” was newly created and its attribute was defined with “Radius” being 1.5 mm. The “Cylinder” was the screw channel pole, which can simulate the channel for screw passing through (Figure 1A). In the transparent view, CAD Objects were selected and the radius of the “Cylinder” was adjusted to be 2 mm. The diameter of the “Cylinder” can be rotated at any angle or increased. Caution was taken to avoid destroying the bone surrounding the screw channel, and the scheduled ideal position of the entry point was located by repeated adjustments. The entry point was about at 1 mm posterior to the midpoint of inferior-anterior margin of the C2 vertebral body. The distance between entry point to the tip of the odontoid process and the axis for screw insertion were determined using the Measurement Distance function. The support column (radius 7 mm) was designed based on the screw channel pole (Figure 1B).
The navigation module was composed of a screw channel pole, a support column and a solid object. After Boolean operation, a prototype of navigation module was obtained. After trimming unrelated parts, an ideal navigation module with screw channel was achieved (Figure 2).
The STL format file of the navigation modules was processed by 3D printing software MakerWare version 2.4.1.24. Under high print precision mode (print precision: 0.1 mm), polylactic acid navigation module products were 3D printed, screw channel was dredged and the fitting of navigation module product was observed (Figure 3).
The navigation module was closely attached to the surface of the bone of the C2 vertebral body in the field of operation and fixed by compression using fingers. The Kirschner wire was advanced through the navigation module till the posterior-anterior margin of the C2 vertebral body.
After screw insertion, the entry point and orientation as well as whether screws penetrate the cortical bone were observed. X-ray and CT scans were used to determine whether the entry point, orientation, depth of placement and diameter of screws were consistent with those ideal parameters simulated by Mimics software.
Main outcome measures
X-ray and CT scans were used to determine the accuracy rate of screw placement.
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
Odontoid fracture accounts for 9-15% of all cervical spine structures[10], with a mortality rate of 5-10%[11]. There is a consensus that the surgical indications of odontoid fracture[1, 3, 12] include unstable Anderson II odontoid fracture, in particular those displaced fracture (displaced over 4-6 mm in distance or > 10° in angle); unstable comminuted Anderson III odontoid fracture; odontoid fracture accompanied by rupture of transverse ligament of the atlas; odontoid fracture accompanied by atlas fracture, leading to occipitocervical instability; displaced fracture for which reduction is impossible, nerve compression-caused neurological disorder; obsolete odontoid fracture, bone nonunion, or atlantoaxial instability. Surgical contraindications include (1) comminuted fracture of the base of odontoid process, severe osteoporosis; (2) rupture of ligamentum transversum; (3) oblique fracture. In addition, it is disputed whether long-term (> 6 months) odontoid fracture is a contraindication[3, 13-14].
The MedCAD function of Mimics can visually simulate the odontoid screw fixation. First, the entry point and orientation of screw can be simulated. According to measurement parameters, the diameter and length of placement of cannulated screws are designed. The simulated odontoid vertebra can be rotated at any angle, thus, the structure of screw channel, orientation of screw and the anatomical relationship with adjacent structures can be observed from all angles. Once the screw penetrates the cortical bone of the odontoid process at one point, the orientation of screw insertion can be adjusted till the satisfactory position, even the theoretical optimal position. Therefore, the Mimics software provides insights into selection and preparation of therapeutic protocol for clinical surgeons[19].
3D printing technique sets up a bridge between virtual design and clinical practice and has been widely recognized as a method that is accordant with the concept of individualized medicine. Paiva et al [8] applied 3D printing technique in one patient with cervical Ewing’s sarcoma and they considered that this technique benefited for preoperative scheme preparation and intraoperative risk evaluation.
The Mimics software helps design module: The Mimics software has been widely used in daily teaching and research, is easily learned and convenient for popularization because of its short learning curve. It can to the largest degree reduce data loss risks produced during transformation by multiple software formats[22].
Achieve one-time successful implantation and reduce radiation damage: avoid the formation of false or excessively wide screw channel caused by determining entry point or adjusting guide pin orientation too many times; ensure suitable and firm fixation of screws; reduce the incidence of screw loosening, shedding and fragmentation; avoid the occurrence of a series of adverse events caused by repeated operations, including iatrogenic injury of C2-3 intervertebral discs, destroyed blood supply around the fracture line, worsened displacement and rotation of distal end of fractured odontoid process and spinal cord injury; reduce X-ray device use and avoid operator’s and patient’s long-term exposure to X-rays.
CT scan layer thickness and quality of specimens: the thinner layer, the higher level of integrity of three-dimensional reconstruction models, and the more satisfactory attachment of the navigation module designed according to the bone surface of reconstructed module to cadaveric vertebral spine, on the contrary, thick layers lead to rough surface of three-dimensional models, resulting in unstable attachment of guiding module and finally influencing the optimization of screw placement. If the sclerotin of cadavers is poor, scan data can be supplemented by the Mimics software, thus a bias between virtual design and practical specimen possibly occurs.
and other pedicles of vertebral arch or into internal implantation in other regions and demonstrate wide clinical application prospects.
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||